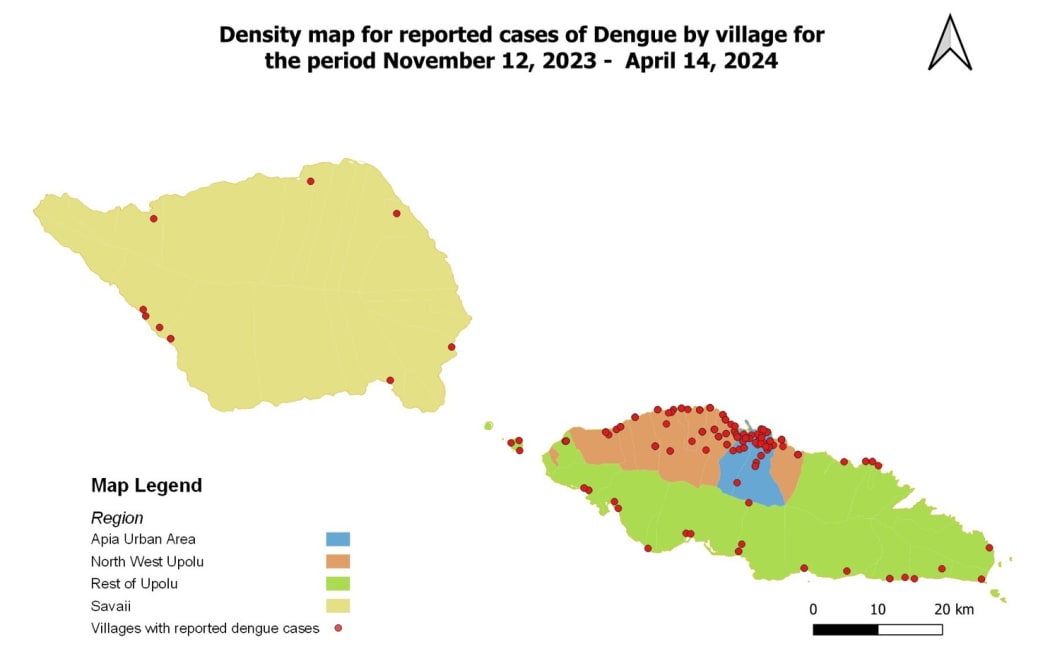
Reported cases of dengue fever in Samoa, November 12, 2023 to April 14, 2024. Photo: Samoa Ministry of Health
A medical advisor from New Zealand's Immunisation Advisory Centre says dengue is expected to increase with climate change and urbanisation.
In its report for the period of 1-14 April, Samoa's Ministry of Health the country had 216 laboratory-confirmed cases from November last year to the end of that two-week reporting period.
There were 82 new cases were reported in the two weeks to 14 April.
Dr Joan Ingram said cases of dengue have increased over six-fold since 2000.
"It is expected that cases will continue to increase with climate change and urbanisation," she said.
"Between 2012 and 2021 there were 69 outbreaks of dengue fever among the Pacific Islands."
She said after an infected mosquito bite there is an incubation period of 5 to 7 days (maximum 10).
Dengue infection may be unnoticed, or a mild illness or significant illness with fever, pain behind the eyes, bone, joint and muscle pain, and sometimes rash, vomiting and diarrhea.
"In up to 5 percent of infections - most often after a second infection - serious complications such as bleeding or shock can arise.
"There are four different dengue viruses, and infection with one gives long-term protection from that virus, but may make the illness following one of the other three dengue viruses more serious."
World Mosquito Programme director of global delivery Cameron Simmons said Samoa, like most other countries in the Western Pacific, has a long history of being impacted by dengue outbreaks.
He advocated for the Wolbachia method, developed by his organisation, which gives mosquitoes the bacteria to reduce their ability to transmit dengue, Zika and other viruses.
"We know that insecticides and environmental clean-up campaigns can help a little to control the outbreak, but they are short-lived interventions that will not stop future outbreaks in Samoa.
"This most recent surge in dengue case numbers is troubling because the case numbers will inevitably increase, stressing the health system and hurting the wellbeing of patients and their families."
Health advice
Samoa's Ministry of Health recommends cleaning up stagnant water sources, wearing clothing to minimise mosquito bites, and using mosquito nets and repellants.
Half a day this Friday will be dedicated to the dengue-related clean-up of public spaces and government buildings.
The ministry's acting director general Dr Glenn Fatupaito said the clean-up is an effort to eradicate mosquito breeding grounds.
"The idea is the different ministries surrounding the areas just clean up areas and waterways, any place that holds water, potential breeding grounds and such," he said.
He also said pot plants can be a breeding ground for mosquitoes, as certain plants hold water.
"It's one thing that was also discussed - people love Bromeliads, especially in Samoa.
"If you're going to plant such plants, keep it at least 100 yards from your household to reduce potential breeding grounds for mosquitoes."
The health ministry is also urging households to look out for their high-risk family members.
"We're mindful of our very old, our very young, our pregnant women as well," Dr Fatupaito said.
"We don't want any complications, and if you're sick: the supportive treatment, bedrest, lots of fluids, paracetemol, and come see a doctor if things are getting worse."
He said with numbers expected to rise, the Ministry will release weekly online updates starting on Friday.
New Zealand's Safe Travel website is suggesting anyone travelling to, or living in, Samoa should have comprehensive medical and travel insurance policies.













